Since 4K monitors and TVs have been released, and with the arrive on the market of faster and faster SSD units, there will always be a more intense need to use performing connection interfaces, which can provide their contents satisfactorily. Notebooks, on the other hand, are always getting lighter and more compact, often at the expense of connectivity.
Ports and cables available today, do not let you keep pace with the constantly higher band request.

Thunderbolt 3 changes everything by revolutionizing the scenario. The interface now uses – in its third version – the new USB Type C connector, making the connection of every type of device possible then.
Thunderbolt was born in 2011 from a cooperation between Intel and Apple. At that time, the USB 3.0 interface was able to transfer data up to 5 Gbps (or 640 MB/s) while the first generation of Thunderbolt offered twice that bandwidth (10 Gbps).

Thunderbolt, then, differently from USB, lets you transfer multiple kinds of data: it doesn’t just make a serial data transmission to storage media or hardware devices, but can also transfer video signals to monitors and display in general.
Thunderbolt’s interface lets you, also, activate a daisy chain: it means that you can connect, for example, a storage device to the computer and then connect a display to it. Each device will work as expected.
Originally designed to improve USB 3.0 features, Thunderbolt used a mini DisplayPort that Apple implemented right away, in 2011, on its MacBook Pro. Due to production costs too, the usage of Thunderbolt connector always remained a niche choice, ad only a few systems implemented it.
What the USB Type-C connector is
USB Type-C is the new connector, designed to replace the omnipresent Micro USB that is located, for example, on every Android smartphone, but also on many other devices. The aim, during time, is, also, to replace the very popular USB Type-A connector, best known as the most typical USB connector.
The USB Type-C connector is compact and pretty small sized, but its main, and new, feature is reversibility: there’s no more an unique way/side to insert the USB cable. Moreover, USB Type-C lets you eventually supply connected devices by transferring more energy: starting with the 2,5 W of USB 2.0, or the 4,5 W of USB 3.0, we got to the 7,5 and 15 W of USB Type-C. It’s just about default values, though: where needed, in fact, USB Type-C could transfer up to 100W, being able to recharge even notebooks.
In the article about how to recognize USB, USB Type-A and USB Type-C ports, we highlighted all the main differences between USB Type-C and the previous ones.
Thanks to USB Type-C, smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices can be recharged very quickly, and the same cable used to supply a notebook may be used to connect many devices.
In theory, it will be possible to recharge your own smartphone by connecting it to a tablet, a notebook or any other mobile device: this way, you may restart your device right away, if the battery level isn’t enough to turn it on.
Thunderbolt 3 plus USB Type-C connector: dawn of a new era
Instead of mini DisplayPort previously chosen, Thunderbolt 3 uses USB Type-C. It’s a very important choice, and a pretty right one, for a few reasons:

- Thunderbolt 3 “frees itself” from the niche sector it used to belong to. Apple has been the only society to really support Thunderbolt interface. Thanks to the usage of the USB Type-C connector, anyway, things are now going to change. Thunderbolt started now to show itself through many notebooks and ultrabooks; as a consequence, a strong increase of the products implementing it, results in increasing the number of compatible devices.
- A widespread distribution of Thunderbolt 3 is a good news for USB Type-c too. USB Type-C cables, in the end, let you transfer a larger amount of energy and are equipped with a reversible connector. Thanks to Thunderbolt, though, their potentialities get highly improved.
We must say that not all the USB Type-C ports are Thunderbolt 3 compatible: an hardware that doesn’t use an Intel Skylake cpu, has no Thunderbolt controller (most of the mobile devices do not use Intel technology).
By connecting an USB Type-C device to a Thunderbolt 3 port, this will work but won’t be able to take advantage of Thunderbolt’s interface features.
Similarly, a Thunderbolt 3 device, connected to an USB Type-C port, works but cannot use Thunderbolt features.
Thunderbolt 3 support has been implemented on Intel Skylake chipsets released at the end on 2015.
Features of Thunderbolt 3
Thunderbolt 3 offers the opportunity to carry out lots of operations with a single cable: extremely versatile, the interface lets you connect displays, storage devices and many others.
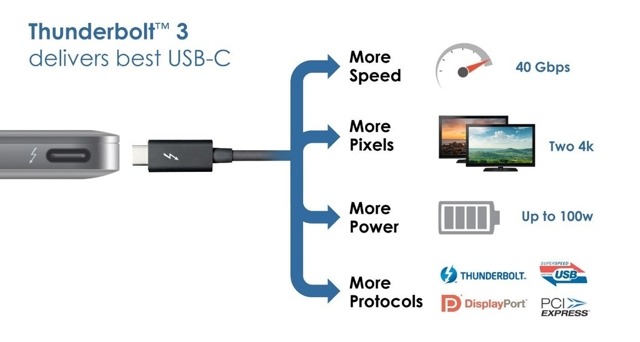
Since Thunderbolt 3 supports the last DisplayPort specs, it is possible to use a single cable to manage two 4K displays at 60Hz (4K monitors’ hallmark is a resolution which is twice as the “Full HD” 1080p one).
Unless you don’t use a “daisy chain”, cables will have to be separated to reach the two monitors, but only one Thunderbolt cable will be connected to the computer.
Thunderbolt 3 interface is, also, unbeatable in terms of data transfer speed. You can even think about the purchase of an external case to put two hard disks or SSD unit, and lets you set up a RAID configuration.

Thanks to the Thunderbolt 3 connection, you may get a data transfer speed up to 785 MB/s, sending streaming contents to the connected 4K monitors, at the same time.
In case you want to focus on storage needs, you may get data transfer up to 5GB/s; performances that are 8 times better than USB 3.0 and 4 times better than USB 3.1.
The bottleneck, then, will be about the hard disk performances, and not the cable or the interface itself.
How to increase the performance of the computer’s graphic card with an external box
Products like Razer Core well highlight the possibilities offered by Thunderbolt 3.

Razor Core is a eGFX box, that is an external device which increases the features in terms of graphic elaborations of the system in use. The connection is made through Thunderbolt 3 interface: a compact and light notebook could immediately turn into a powerful 3d rendering or gaming machine.
Even if the band offered by Thunderbolt 3 isn’t really comparable at all with the one offered by PCIe interface, devices like Razer Core could pretty amazingly increase performances, for example, of any notebook.
Read More:
Best Gaming Monitor